February Review
By Adam Novakovic, Energy Markets Consultant
In what proved to be the wettest February in 258 years, we saw energy prices continue their downward trend. Electricity prices for the upcoming summer season fell approximately 20% in the first 3 weeks of the month before ending the month with a small rally in a pattern mirrored by the gas prices.
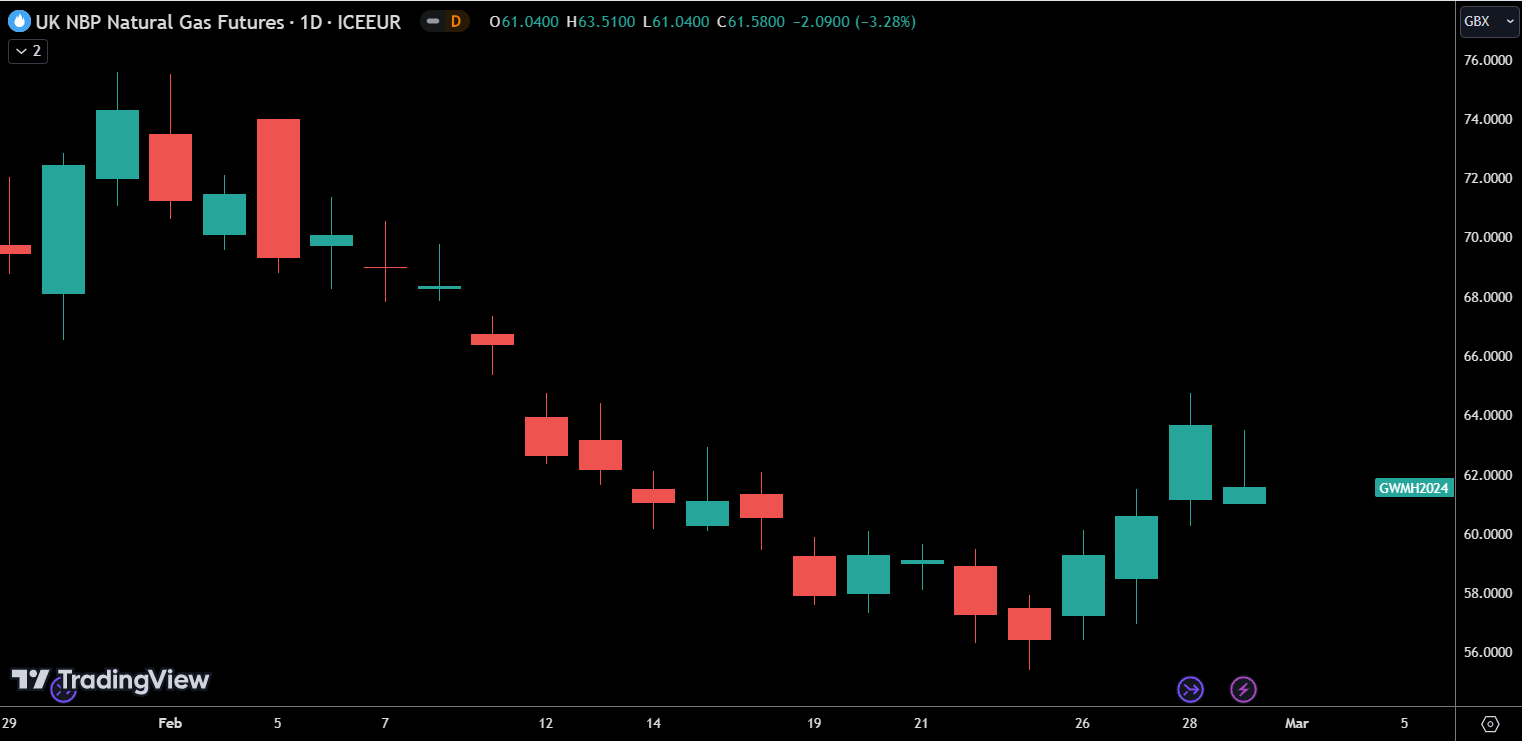
The energy markets saw prices pull back to levels not seen since 2021, although after 7 weeks of the price falling some counter movement was to be expected. For companies on flexible contracts who are looking to make purchases, the 2nd and 3rd weeks of February represented an ideal time to lock in prices as the market achieved a short-term bottom. The end of the month rise seems likely to be caused by parties looking to de-risk and lock in prices while they are at these lows. The downtrend could very well be set to continue after this period of de-risking, but there now appears to be a greater risk to the upside than there is potential for large decreases.
One of the primary reasons for this continued decline in price was the milder than expected weather in February. While it may have been wet, windy, and unpleasant, it wasn’t quite as cold as had been feared, which led to lower levels of gas consumption throughout the month.
The market also appears to have developed further resilience to negative news on the supply side. The first week of February saw a halt in exports from Norway’s Nyhamna processing plant. A power outage at the plant coincided with a compressor failure at the Troll gas field, which further reduced Norwegian export capacity. In the previous 3 years events such as this have caused sharp spikes in price. As recently as a few months ago, threats of industrial action at an Australian LNG plant caused prices to rise sharply. However, it seems faith has been restored in the UK’s ability to deal with some small supply-side shocks.
Part of this ability to deal with supply issues is related to decreased demand. Reports released in February showed that gas demand had decreased 20% across Europe since the Russia-Ukraine conflict began. Rising prices have made both individuals and businesses more conscious of how they consume energy, and consumption patterns have noticeably changed as a result.
One threat to the supply-side which may have an impact in the future is seabed warfare. Reports this month have highlighted attacks on subsea connections as a potential security threat to the UK. China and Russia were mentioned as countries that have sufficiently advanced technologies in this area, an area that the UK may be under-prepared for. Should we see seabed warfare increasingly occur, it could be a case that this becomes one of the major threats to the UK’s energy supply.
Outlook
As a result of the previously mentioned lower demand, UK reserve levels remain in a healthy state. As such there appears to be no need for large purchases to replenish these levels, which suggests the downtrend could be likely to continue into the summer months.
The conflict in the Red Sea still remains a risk. While we saw further Houthi attacks on commercial vessels this has yet to impact LNG exports out of the region. The threat of Lebanon and Iran being pulled into any escalating conflict should be a cause for concern though, and any developments will need to be monitored closely.
The end of month buying doesn’t appear to suggest a change in trend, merely some expected buy-back after a prolonged period of decline. This may continue into the first few days of March, or we may a slightly longer period of price stability, but it seems after this period, the decline in price will likely continue. For those with flexible contracts this month has presented good opportunities to make purchases, but further declines seem probable, albeit with there now being an asymmetrical element of risk should the market encounter a supply-side problem of significance.
If your business requires advice with its energy procurement, management, or planning, then don’t hesitate to contact Seemore Energy to speak to experienced advisors who can help you with bespoke strategies and advice that is tailored to your needs.